Difference between revisions of "Getting connected on Github"
Mark Thomas (talk | contribs) |
Mark Thomas (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
At this point, command is “in” the Lattice-Vibrations folder, and is ready to carry out commands from there. | At this point, command is “in” the Lattice-Vibrations folder, and is ready to carry out commands from there. | ||
If you’d like further advice on how to navigate in command, check out: | If you’d like further advice on how to navigate in command, check out: [https://www.git-tower.com/blog/command-line-cheat-sheet/ command cheat sheet]. | ||
Once you’ve opened the file you created earlier, enter <code>git clone <nowiki>https://github.com/Imperial-visualizations/Lattice-Vibrations</nowiki>. git</code>. Now that you have a local repository! You can now look at the code of the visualization in an IDE of your choice (most of us use VSCode). | Once you’ve opened the file you created earlier, enter <code>git clone <nowiki>https://github.com/Imperial-visualizations/Lattice-Vibrations</nowiki>. git</code>. Now that you have a local repository! You can now look at the code of the visualization in an IDE of your choice (most of us use VSCode). | ||
Revision as of 14:33, 15 July 2021
This page details how to get started coding.
The GitHub
Before you get started and connected, you may want to see some of our current visualisations on https://impvis.co.uk/teach our website! GitHub is used to store all of the code used to create the visualisations. Once the developer (you) has set up a repository on GitHub, either command or GitKraken are used to make a copy of the repository on GitHub and store it locally (on your computer). From here, you can edit it. Communication between collaborators of a particular visualisation is Slack is used to communicate with all the collaborators of a particular visualisation. We use Trello to keep track of all the tasks that need completing to move forward with a visualisation. Documented below is how to use all of these tools and services: Summer team:
Github:
We store and share our visualisations code on Github.
If you don’t have a GitHub account, follow the instructions here. You will need a new username and an email address; your college email should be fine! Once you have completed your setup (don’t worry too much about customization along the way), you will receive a verification email on your registered email account. Open the email and click “verify email address.” Doing this will open GitHub logged into your new account and ask what you want to do first. If you wish to learn more about GitHub, you can follow one of their suggested options. However, you can skip if you only want to use GitHub for imperial visualisations for now.
Command and Gitkraken
Once you have a GitHub account, you can clone the repository (copy it to your local computer), make changes, and upload them to GitHub so that your changes get updated.There are two classic ways that we do this at Imperial Visualisations. One way is using command, and the other is using GitKraken.Command and GitKraken are equivalent methods to allow communications between your machine and our GitHub. Command (or Terminal) uses line commands, while GitKraken is an app that has all the equivalent actions.
Both have their pros and cons; for example, GitKraken is more visual, has a shallower learning curve, and less to remember to use it. On the other hand, command works much faster and is more straightforward to fix the level of issues dealt with in code & crisps. If you continue programming in the future, you will most likely need to know how to use command eventually. You also look more like a hacker when using command. For further information about the benefits of using Gitkraken and Command, check out this comparison (by GitKraken...) https://support.gitkraken.com/pdf/infographic/gitkraken-vs-cli.pdf. We do not have a preference for which one of these you use, half of us recommend using Command, the other half Gitkraken. The choice is yours!
Once you have chosen, there are a few steps that you need to go through in order to make changes to files on GitHub. Here are some instructions on how to each step necessary to create and make changes to files you want on GitHub.
Step 1: Downloading the service
Command: Congratulations, you already did - this is built in as Command Prompt on Windows or Terminal on MacOS. GitKraken: To download GitKraken, please visit https://www.gitkraken.com/download and download it to a location you will remember.
Step 2: Opening the service and signing in
Command: You may search in your machine for Command Prompt or Terminal.
GitKraken: Open a GitKraken window from wherever you saved it. Opening GitKraken can sometimes take a few minutes. Once you see the image to the right, click “Sign in with GitHub.” That should take you to a screen which looks like picture 2.
Click “Continue authorization.” That should take you to a GitHub login page (picture 3).
Use your already made GitHub username and password. If you authorized your email for your GitHub account earlier, then signing in correctly there will take you to the page as seen in picture 4. Click “Authorize Axosoft.” Once you have done this, you will see
This means you can safely close that tab and go back to your Gitkraken window. Opening this will take you now to “Set up your profile,” where you choose your avatar and account name. Go ahead and agree with the terms and conditions. No need to start a free trial of GitKraken pro, their free version does everything we need.
Step 3: Cloning a repository (in command)
In order to access the desired repository, we must clone it onto your local computer. To clone a REPOSITORY owned by USERNAME, use git clone https://github.com/USERNAME/REPOSITORY our local computer. To clone a REPOSITORY owned by USERNAME, use git clone https://github.com/USERNAME/REPOSITORY (Note, press enter to execute commands). For example, if I wanted to clone a repository such as “Lattice-Vibrations” I would do the following:
- Create a folder on my computer with which I would like to clone the repository e.g., ImpVis_projects
- Then in the command line navigate to the folder you just created.
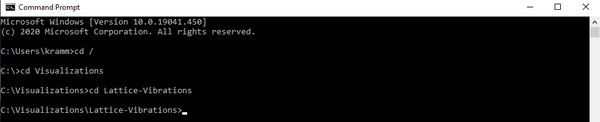
Note, to navigate in command, Use cd directory to navigate into a folder from the current folder you’re in. If you make a mistake, use cd .. To navigate to your root directory, use cd / An example: For me, the writer, say I wanted to reach my “Lattice Vibrations” folder in command, and say the root to that folder was from the C drive which contained a folder “Visualizations”, which contained the “Lattice Vibrations folder”, then I’d use: 1.) cd / to get back to the C drive. 2.) cd Visualizations to open “Visualizations”, then 3.) cd Lattice-Vibrations to get into the “Lattice-Vibrations” folder. In Command, that would look something like
At this point, command is “in” the Lattice-Vibrations folder, and is ready to carry out commands from there.
If you’d like further advice on how to navigate in command, check out: command cheat sheet.
Once you’ve opened the file you created earlier, enter git clone https://github.com/Imperial-visualizations/Lattice-Vibrations. git. Now that you have a local repository! You can now look at the code of the visualization in an IDE of your choice (most of us use VSCode).